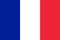
Valgus deformation of the foot in children is a pathology in which the distance between the inner sides of the ankles is 4-5 cm or more during tightly compression and straightening of the legs.At the same time, the heel, along with the fingers, deviates from the outside, and the internal arches of the legs seem to be flooded inwards.

In the orthopedics, such a curvature of the legs is called X-shaped (with deformation of the varus on the legs, on the contrary, O-shaped curvature is observed).If Valgus deformation is noted a decrease in the height of the arches of the steps, they say it is a deformation of flat valgus.
Usually, parents are noticeable about the deformation of Valgus on the foot in their child when he or she performs seven to eight months-for this period, the first attempts at independent walking are input.If you look at the picture of the deformation of your feet with a flat volgus, you can notice that the legs are bent in the knee joints, the fall of the knees, "look" and the distance between the legs is quite large, they fall.
Classification
In medicine, three degrees of weight of the Valgus anomaly are distinguished:
- Light.The height angle of the arch is smaller than 140 °, the height of the longitudinal arch of the stop is about 15-20 mm, the position of the valgus on the back of the foot is about 10 °, the front of the foot is distributed from 8-10 °, the bone of the heel is inclined to 15 °.
- On average.The height of the arch in the second degree of deformation of the valgus of the foot in children is 150-160 °, the height of the longitudinal vault is 10 mm, the bone of the heel is tilted from 10 °, the position of the valgus on the back of the foot and the abduction of the front vault is not more than 15 °.
- Heavy (steps).The height of the vault is from 0 to 5 mm, the angle of slope of the Calcaneus is from 0 to 5 °, the angle of the arches of the arch exceeds 160-180 °, the position of the back and the lead of the front is more than 20 °.The child complains of constant joint pain.The heavy weight of the deformation is not subject to completion of the correction.
There is another classification of valgus deformation of the legs, which is based on the cause of the disease:
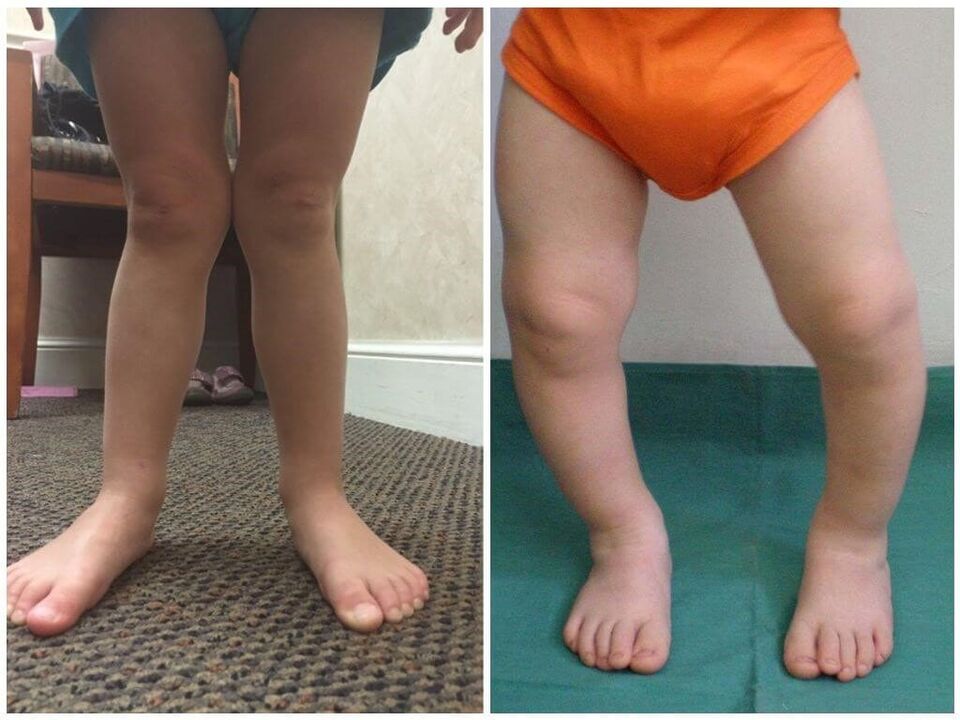
- Compensatory (caused by a shortened Achilles tendon).
- Structural (due to the congenital incorrect position of Aries bone).
- Spastic (is a consequence of muscle cramps that occur due to disorders of cerebral cortex).
- Corrective hyper (caused by illiterate treatment of the infant curvature of the foot).
- Rachitis (manifests itself in children with rickets).
- Paralytic (complication of encephalitis or polio).
- Traumatic (caused by fracture of the bones of the ankle, rupture of the ligaments).
Causes of Valgus Deformation in Children
Valgus deformation of the foot is congenital and acquired.In the first case, the causes of the disease are related to the intrauterine disorder of the location/form of the bones.The diagnosis is made at an early age.
The acquired form of the Valgus anomaly is not caused by the end tendons, as well as the deviations in the development of the musculoskeletal system.Usually, the diagnosis of "Valgus deformation of the stop" is made by eight months or when a small patient is 1 year old.The deviation is most often formed in weakened children with muscle hypotension.
Among the most common causes of valgus deformation of the step in the child:
- unobstrunce;
- intrauterine hypotrophy;
- Frequent diseases with bronchitis, acute respiratory viral infections, pneumonia;
- congenital weakness of connective tissues;
- rickets;
- Ligament injuries, lower legs, muscles;
- Long stay in gypsum;
- Obesity of children;
- too early place the child on the feet;
- Wearing poor quality/improperly selected shoes.
Also as a result, the anomaly of Valgus occurs:
- Cerebral palsy;
- Polyneuropathy;
- osteoporosis;
- dysplasia;
- endocrine and genetic disorders;
- congenital thigh dislocation;
- polio;
- Muscularis Dystrophia.
Valgus deformity symptoms
Symptoms of Valgus deformation of the foot in children include:
- As he walks, the child does not step on the whole leg, but only on his or her inner edge (the legs are "flooded" inwards).
- The legs take shape with X-shape.
- The gait becomes uncomfortable.
- The child complains of leg pain, back.
- In the evening, swelling of the legs, cramps is possible.
- The shoes that the child wears are torn unevenly - first, the inside of the sole is worn.
If you find similar symptoms in yourself, see a doctor immediately.It is easier to prevent the disease than to deal with the consequences.
Diagnostics
To make such a diagnosis as Valgus deformation at the stop, the orthopedist traumatologist examines the child and prescribes a special examination of him:
- Podometre (the method evaluates the load distribution to certain legs of the legs);
- Computer plantography (allows you to calculate the morphological parameters of the legs);
- Radiography (allows you to study changes in the position of the feet relative to each other).
In some cases, additional ultrasound of the joints is required.In order to exclude the connection of Valgus deformity with diseases of the central/peripheral nervous system, the child is directed to a pediatric neurologist.
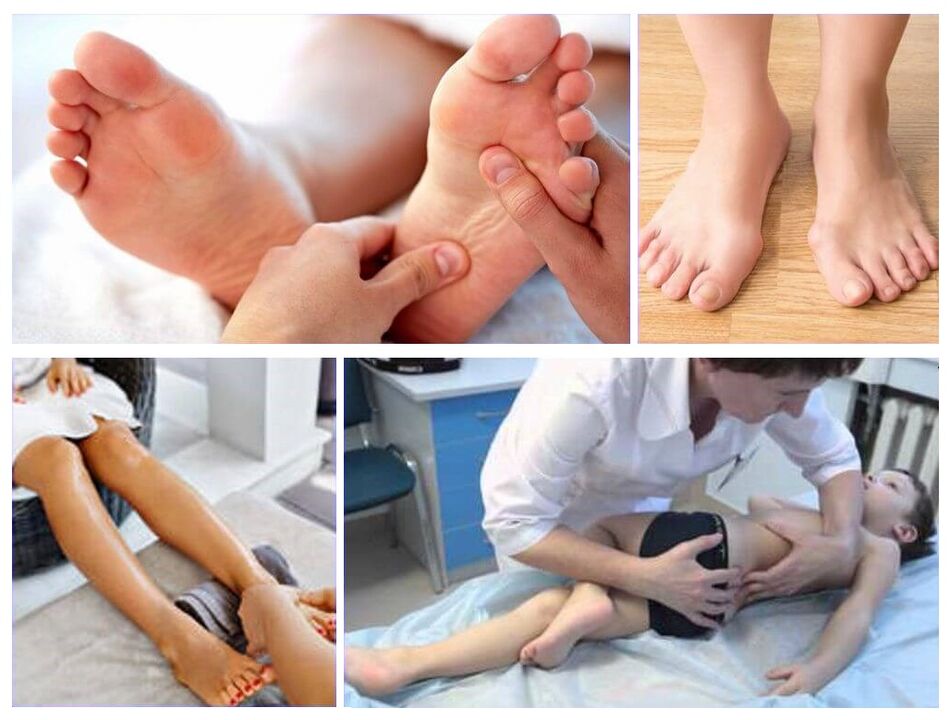
How to treat valgus deformation in children
The treatment of valgus deformation of the legs in children is aimed at normalizing the shape of the legs, restoring their functions, strengthening the ligament and muscular.In the case of a congenital form of the disease, the baby orthopedist may prescribe the wearing of a plaster dressing.Conservative treatment also includes:
- Night Baths.Improve muscle tone, relationships.To prepare the bath, it is necessary to dissolve 1/3 cup of sea salt in 10 liters of warm water.Plant the child in the waist solution for 20 minutes.Sessions are held every other day.One course includes 15 procedures.Repeat the treatment every 4 months.
- Massage.Valgus massage deformation of the foot in children is one of the most important points of treatment.This should be done by a qualified specialist.
- Mud and ozotoceros applications.
- Paraffin therapy.The paraffin sheath is made only on the foot or in the form of a trunk.Heating improves blood circulation, connections.
- Acupuncture.
- Electrical stimulation of the muscles of the foot and lower leg.Encourages muscle strengthening.
- Electrophoresis, magnetotherapy.
- Exercise therapy.LFK with valgus deformation of the foot is done daily.Properly chosen exercises can improve the flexibility of connections, muscle strength, increase joint mobility, normalize tissue metabolism, blood circulation.
In order to correct the deformation of the valguses of the legs, children should wear special shoes with a hard side fixation of the heels and legs, to use individual functional insoles.As for sports, you can ride a bicycle with the Valgus anomaly, swim.
The disease resorts to surgical treatment in extreme cases (7%) if all conservative medical measures are ineffective.Can be:
- Operations for arthrodesis.Provide the fixed joint between the bones of the heel and the talus, which causes the muscles of the inner arch.
- Surgical intervention.The manual adjustment of the child's stop is performed and then plaster is deposited.Sessions are held once a week.After each of them, the foot changes its position.The doctor applies gypsum to the whole leg (starting from the middle third of the thigh).At the same time, the knee is bent at an angle of ninety degrees.At the last session, the doctor fixes the Talus-the adulterial joint in the correct position, introducing the knitting needle through the skin.Then he dressed gypsum for two months.
- Children who have undergone the treatment of valgus deformation of the legs with the help of surgery should always wear special orthopedic shoes that support the arches of the feet.
- Small invasive operations that change the angle between the individual bones of the foot, which causes the tension of the ligamentary apparatus.
Hazard
If the degree of deformation is mild, full recovery is possible.The severe degree of deformation of Valgus is not an ordinary cosmetic defect.The disease causes serious functional impaired limbs, which can lead to damage.
The lack of competent treatment of an anomaly can cause:
- flat legs;
- constant pain in the legs;
- osteochondrosis;
- arthrosis;
- shortening of the limbs;
- storage disorder (scoliosis);
- Deformation of the joints of the pelvis, ankle and knee.
Risk group
The biggest risk of getting Valgus deformation arises if your parents put the child early on their feet (up to 9 months), buy him bad quality shoes or size is incorrectly selected.Also, babies suffering from rickets, with a genetic predisposition to curvature, are also prone to pathology.
Valgus prevention deformation of the foot
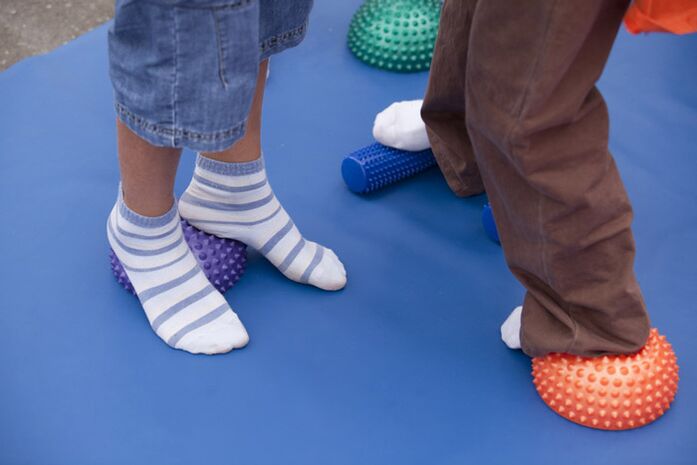

Prevention of the disease includes the following points:
- You should not put your child on your feet for up to 9 months.
- Exclude the development of rickets (preventive intake of vitamin D).
- Buy shoes with orthopedic insoles.The background of children's boots should be 3-4 cm higher than the heel.The approach should bend well.A prerequisite is the presence of a manager.
- Massage your feet.
In addition, you should not ignore the planned examinations of an orthopedist, surgeon, neurologist.At the age of 1 month, the doctor may diagnose the presence of congenital skeletal diseases, after 3 and 6 months to exclude the development of rickets, at 1 year to evaluate the volume of joint movement, the correctness of the vertebrae, at 3 years - check the staging, posture and measurement of the length of the limbs.
It is impossible to quickly recover with the diagnosis of Valgus deformation.Parents will be able to evaluate the first results not early six months after the onset of conservative therapy.
This article has been published exclusively for cognitive purposes and is not a scientific material or professional medical council.