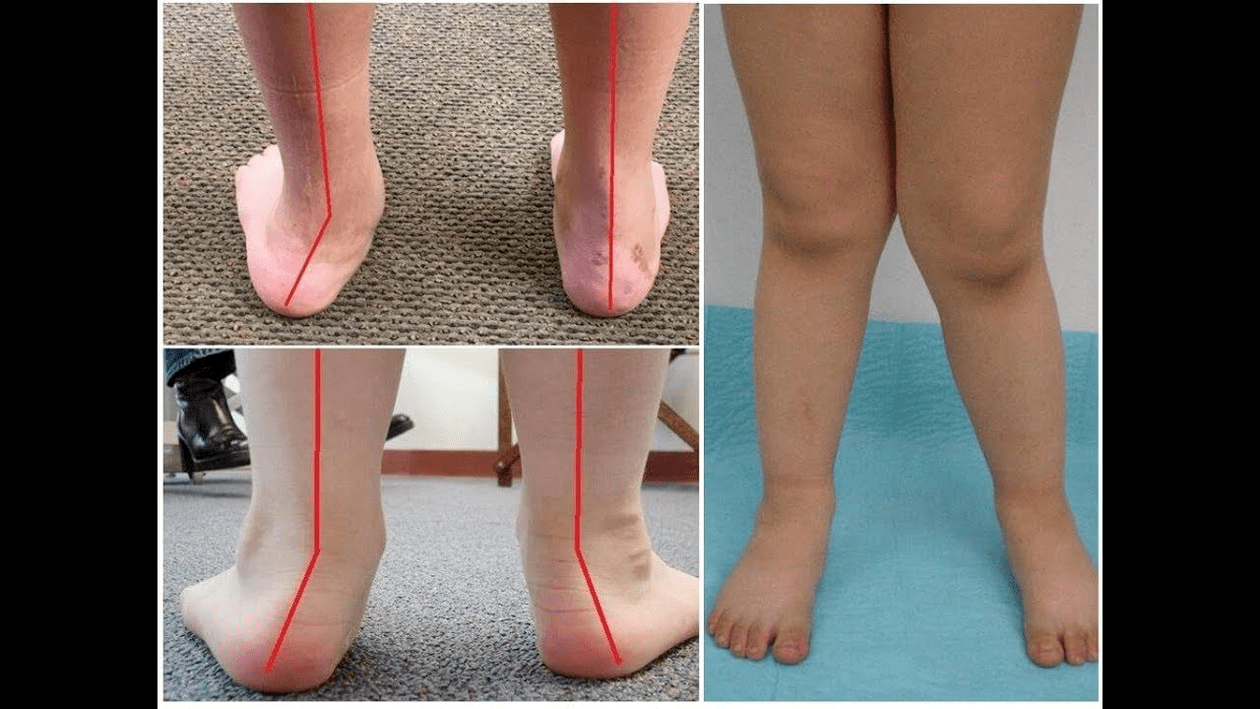
Valgus deformation of the steps is most often congenital. In some cases, however - with paralysis, traumatic lesions - can occur in the mature period of life. The main symptoms of the pathology are soreness in the area of the legs and muscles of the lower leg, a visible disorder of the shape of the legs, and a change in gait. The diagnosis of the disease is carried out using a clinical examination, X -treatment, electromyography, etc. Treatment includes conservative and surgical methods. However, proper efficiency is observed only in reconstructive operations.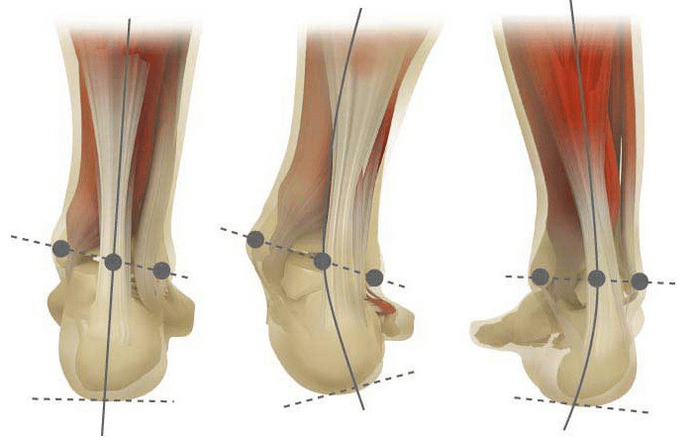
Valgus deformation is the curvature of the foot characterized by the equalization of its longitudinal arch. Usually the inner edge of the foot is descended ("drops") and the heel turns out.
The step of a person, by virtue of his location, acquires the pressure of the entire mass of the human body. For this reason, it has a special anatomical structure that allows depreciation, balancing and stabilizing movements. However, an important component for performing these tasks is the correct form of stopping.
Today, the most important problem of traumatology and orthopedics is the deformation of valgus on the foot. The meeting is estimated at 30-58%, where 2/3 of cases make up congenital disorders.
The pathology is largely socially significant as it covers all age groups of the population and also helps to curl the spine, the early development of osteochondrosis and arthrosis of the joints of the lower limbs.
When you take your feet (if you look at them from the back), a deformation of X is formed at the level of the ankle: the ankles are in contact while the heels are 5-6 centimeters apart.
Most often, the pathology is congenital by nature and is diagnosed in children back to the hospital (or immediately after the start of walking). Such a condition is regulated for up to 5 years, after which (in the absence of proper treatment), the child develops flat legs.
It is believed that the main cause of valgus deformation of the foot is an inadequate function of the posterior tibial muscle or weakness of the ligamental apparatus.
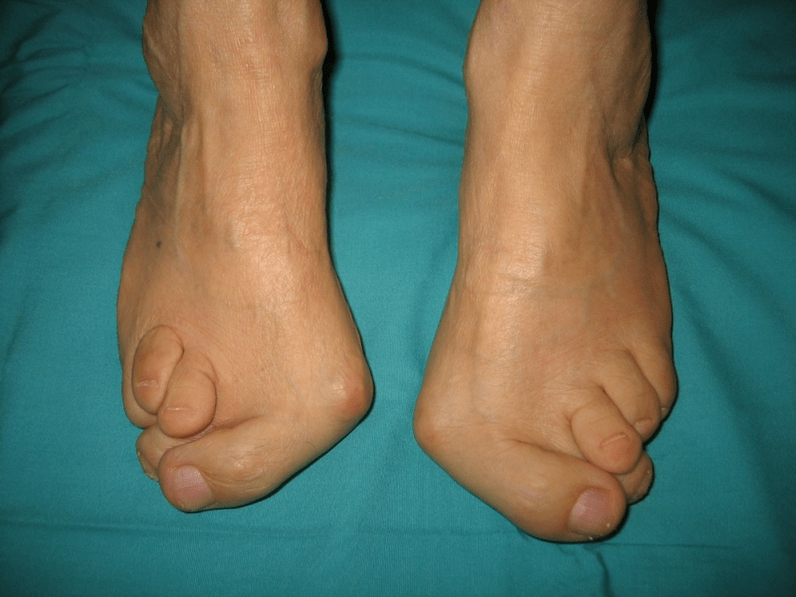
Today, other factors are distinguished in the development of pathology: The development of the pathology is also facilitated by improperly selected shoes or excessive correction of the club in childhood. The severity of pathology (the power of manifestation) is divided into degrees: Depending on the participation of certain structures, the following stages of curvature are distinguished: In the first stage, patients are disturbed by periodic pain after prolonged walks or long vertical loads (standing or sitting on the foot). As a rule, pain syndrome is enhanced when walking in improperly selected shoes. The next stage of the disease is related to the appearance of the curvature of the foot: patients in the standing position do not rely on the outer edge of the foot, but with its entire area. There is a slight change in gait. In the third stage, the protruding of the thawed bone is determined (noticeably the lower ankle on the inner surface of the ankle), as well as a strong deviation of the heel outside (the patient is based on the inner edge of the heel bone). The advanced deformation of Valgus of the feet is characterized by a pronounced curvature of both the leg itself and the ankle joint. Patients complain of severe pain in the lower leg muscles, as well as a significant impairment of the gait: the knees rub against each other until the right and left legs are located at some distance. The severe curvature of the steps is often complicated by deformity of the spine (scoliosis with different positions of the shoulders and wings of the pelvis), osteochondrosis (damage to the intervertebral disc with hernia formation) or arthrosis (premature wear of the intraaric carpet. The diagnosis of the curvature of the foot consists of: Additional consultation of a neurologist (with deformities due to cramps or paralysis), endocrinologist (in case of diabetes or thyroid disorders/parathyroid gland) and gynecologist (when the threat) may be required. If the curvature of the foot appears against the background of osteoporosis, densitometry is required - bone density examination. Among the main methods of treating Valgus curvature of the legs are conservative and surgically. Do not destroy sore joints with ointments and injections! Conservative approach This type of help is aimed at getting rid of the symptoms of the disease, but does not eliminate the root cause of the pathology. The technique includes: Conservative methods also include physiotherapy procedures (ozocket, paraffin applications, electrophoresis, magnetic effects), massage and a complex of physiotherapy exercises designed for a specific clinical case. Watch out! Today, most experts prefer surgical treatments because conservative therapy is ineffective (according to statistics, it is useless in 60% of cases). Surgery
The volume of work and its type depend on the direct stage of the disease. Thus, the first degree of deformation of Valgus is treated by synavectomy (removal of the tendonal sheath for adjusting the total tension) or osteotomy (dissection) of the heel to return to the anatomically correct position. In the second stage of the development of the disease, a transplantation of the tendon turns of the fingers is used. Such intervention is usually performed against the background of dissection of the heel or arthrodesis with an ram with ram (surgical immobilization of the joint between RAM and scaphoid bones). Grade III curvature requires arthrodesis of several joints on the foot at a time: a hassle -free, five cup of cubes and decisive RAM. Such a three -dimension of immobilization is often supplemented by dissecting the bone of the heel. In the IV stage of the pathology, reconstructive operations are needed not only on the foot but also on the ankle. In this case, the instability of the ligamental apparatus is regulated by transplants (from their own body or artificial materials). The volume of operations on the leg itself is the same as at the III degree of curvature.
Recovery period Rehabilitation involves walking without maintenance of the operated leg for 2 months. At the same time, the patient should wear a movable plaster for a long spill of 1, 5 to 3 months. Active movements in the working leg are recommended to start 1, 5 months after surgery. By the 3rd month, a complex of strengthening physical education is introduced. Subsequently, however, patients are forbidden not to be unequal walking and active sports activities. It is worth noting that it is possible to assess the end result of the operation only six months later. Prevent Valgus deformation of the stop includes the following measures: Preventing the progression of the disease is to use conservative methods and early reconstructive operations. In this case, physical activity is limited to prevent the destruction and curvature of the ankle joints. Remember that timely treatment of valgus deformation of the feet not only improves the quality of life of patients, but also prevents the development of osteochondrosis and arthrosis of the knee or hip joint!